I give up. I can’t get the song “Buzzer” out of my head. It’s been days now, and despite my attempts to put it out of my mind it’s affecting me at a deep emotional level. It’s not unusual for me to have a song running through my head now and again, but this one is a little different. I’m getting noodged (smile-out) to write about it, and it’s clear that I’m going to be haunted by this song until I do.
The song very obviously refers to Stanley Milgram’s famous experiment on authoritarianism, and is written from the perspective of a participant – one of the people who “pressed the buzzer” that appeared to give other people increasingly painful electrical shocks.
Controversy surrounded Stanley Milgram for much of his professional life as a result of a series of experiments on obedience to authority which he conducted at Yale University in 1961-1962. He found, surprisingly, that 65% of his subjects, ordinary residents of New Haven, were willing to give apparently harmful electric shocks-up to 450 volts-to a pitifully protesting victim, simply because a scientific authority commanded them to, and in spite of the fact that the victim did not do anything to deserve such punishment. The victim was, in reality, a good actor who did not actually receive shocks, and this fact was revealed to the subjects at the end of the experiment. But, during the experiment itself, the experience was a powerfully real and gripping one for most participants.
Below you can see a video and the lyrics to the song. A higher-quality version of the song is here at NPR, recorded live in concert from WXPN and Wiggins Park in Philadelphia on July 11, 2008. I would be surprised if Dar Williams doesn’t talk about “Buzzer” in the NPR interview, but I’m resisting listening to it until I’ve worked this through.
[youtube width=”400″ height=”343″]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vwvLzG51EWQ[/youtube]
Dar Williams, “Buzzer” (from “Promised Land”)
Sitting with the number eight platter at the restaurant,
Four twenty-nine for almost anything I want,
Add it up, it’s cheaper than the stuff I make myself,
I get by, I never needed anybody’s help,
And I tore out an ad and they told me that I
Would press the buzzer, press the buzzer,
At the graduate lab, they were doing some tests,
I pressed the buzzer, pressed the buzzer.
Ride the circle off of the highway.
Spiral into the driveway,
In the maze of old prefabs
They’ll be waiting at the lab.
I don’t know how everybody makes it through the daily drill,
Paint their nails, walk a dog, pay every bill,
I’m feeling sorry for this guy that I press to shock,
He gets the answers wrong, I have to up the watts
And he begged me to stop, but they told me to go,
I press the buzzer, I press the buzzer.
So get out of my head, just give me my line.
I press the buzzer, I press the buzzer.
Ride the circle off of the highway,
Spiral into the driveway,
In the maze of old prefabs
They’ll be waiting at the lab.
They called me back to the lab to discuss the test,
I put my earrings on, found my heels, wore a dress.
Right away I knew, it was like I’d failed a quiz
The man said “Do you know what a fascist is?”
I said, “Yeah, it’s when you do things you’re not proud of,
But you’re scraping by, taking orders from above.”
I get it now, I’m the face, I’m the cause of war
We don’t have to blame white-coated men anymore.
When I knew it was wrong, I played it just like a game,
I pressed the buzzer, I pressed the buzzer,
Here’s your seventy bucks, now everything’s changed,
I press the buzzer, I press the buzzer
But tell me where are your stocks, would you do this again?
I press the buzzer,
And tell me who made your clothes, was it children or men?
I press the buzzer.
Ride the circle off of the highway,
Spiral into the driveway,
In the maze of old prefabs
They’ll be waiting at the lab.
The opening of the song evokes the character of the singer, a self-reliant northeastern woman of the early sixties. She’s focused on the details of getting through each day, cutting corners, trying to be a responsible person. Seventy dollars for her participation would have been decent pay.
Right from the first chorus, there is something sinister about the people “waiting at the lab,” especially since they are surrounded by all the spirals and mazes in the chorus. The words are reinforced by the melody and the way the sound slows and expands, and the image of the people waiting in the middle of the maze is the last echoing image of the song.
She’s not without compassion. She’s not a sadist. She feels sorry, in a distant sort of way, for the man that she thinks she is training, or punishing, or torturing. His inability to get the answers right is associated structurally with a failure to meet everyday stresses and challenges; an implied judgment is yoked to a certain kind of empathy.
When he begs her to stop, she is told by an authority figure (one of the white-coated men, no doubt) to go on. And she does, without much further comment except the repetition of “I press the buzzer” throughout the rest of the song.
She would have been one of the majority who continued to press the buzzer (the button, the shocker) up to the limits of the experiment. I wonder if this song drew from the testimony of one of the actual participants. Imagine how horrible it would be to realize that you were capable of doing something like this, and not even under any dire choice or extraordinary sense of necessity, but just because there was an authority figure that told you it was all right and released you from attaching any sense of personal ethics and responsibility to your actions.
What a setup. What a perfect, horrifying setup.
It’s no big surprise that the Milgram experiment was controversial. It was a terrible thing to do to people, and I wouldn’t be surprised if some people were affected by it for the rest of their lives. I would be devastated to learn such an ugly truth about myself. But there were some, later, that were thankful for the experience; they learned a deep-down lesson.
62% wouldn’t refuse to continue? The results shocked the world. For many, it seemed to explain how Hitler could have transformed the “good Germans” into a nation that could condone and participate in the events of World War II.
I have always wondered what I would have done. The experiment itself has a high heuristic function, so once you know about it you can never really be sure what you would have done if you had not known about it. I think I would have protested, and then refused to continue – but I have never been totally and absolutely sure. That faint uncertainty in the background adds to my horror and sadness about the experiment – and probably makes the song more emotionally resonant and powerful. Milgram’s study of obedience to authority brought many insights that have been used for good – and for evil – in the years since.
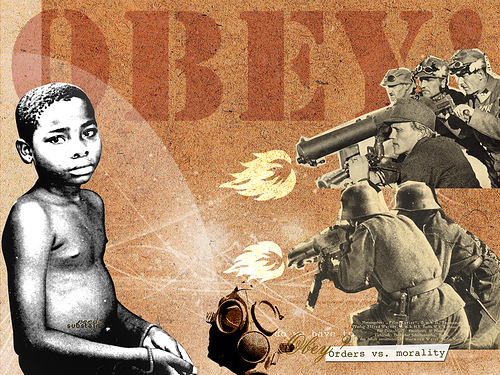
For me, the song centers on the line “we don’t have to blame white-coated men anymore.” It comes after the realization of what has really happened here. Standing there, having failed the life quiz, dressed up in heels and a dress, to realize… But there is a bit of cognitive dissonance here. Yes, she admits it – “I get it now, I’m the face of war” but that doesn’t let off the “white-coated men” at all. Not at all. Mengele did experiments. The U.S. government has done some fairly awful experiments too. And there is a lot of debate in scientific circles about utilizing the results of experiments when human suffering has been involved. Even when the results are valid, it makes one complicit in what was done to achieve those results.
There is a vague undercurrent of anti-intellectualism in the song, which I understand because it strikes back at judgment. “You think you’re so much better than me? You think you’re so ethical. You’re not any better than me. You’d do the same, you people waiting at the lab.” There is a challenge here. “If I’m the fascist,” she seems to be saying, “then as I ask myself, ask yourself too: In what ways are you doing the same? Tell me about your stock portfolio, tell me about who makes your clothes, children or men! Have you stopped to consider all the many compromises we make in our lives every day, the ones that support human suffering under authoritarian power? I’m guilty, but you won’t even think about how you are part of the same system, how you shunt off the responsibility of it.”
An aspect of the Milgram experiment that has always bothered me is how Milgram staged it. Obviously, he couldn’t have Gestapo-uniformed people as the authority figures. I always thought it was an interesting choice to select scientists, people who looked like doctors, maybe. That’s a comment on the scientific community, and on the medical profession – isn’t it? – that they can be switched out for Nazis so easily.
And a further thing. I’ve never been completely satisfied with the explanations given about why a majority of the people continued to administer the shocks. There may be a very small minority who are sadists. Then there are the people who would start to feel uncomfortable. At what point would each person need to be urged to continue? And WHY would they continue? Really why? In his 1974 article, “The Perils of Obedience,” Milgram said:
The legal and philosophic aspects of obedience are of enormous importance, but they say very little about how most people behave in concrete situations. I set up a simple experiment at Yale University to test how much pain an ordinary citizen would inflict on another person simply because he was ordered to by an experimental scientist. Stark authority was pitted against the subjects’ strongest moral imperatives against hurting others, and, with the subjects’ ears ringing with the screams of the victims, authority won more often than not. The extreme willingness of adults to go to almost any lengths on the command of an authority constitutes the chief finding of the study and the fact most urgently demanding explanation.
Ordinary people, simply doing their jobs, and without any particular hostility on their part, can become agents in a terrible destructive process. Moreover, even when the destructive effects of their work become patently clear, and they are asked to carry out actions incompatible with fundamental standards of morality, relatively few people have the resources needed to resist authority.
The participants were not urged with persuasion. Only these statements were used, and in this order:
- Please continue.
- The experiment requires that you continue.
- It is absolutely essential that you continue.
- You have no other choice, you must go on.
The experiment was halted if the participant expressed a desire to stop after all 4 statements. Otherwise, it was continued to the maximum of three 450-volt shocks. Other scientists have confirmed the consistency of the results: 61–66 percent, regardless of time or place, will continue.
How is this to be explained? Really?
What we have are theories, and despite the evidence I see – even from the pseudo-religious right and the flag-wavers and all of those groups who hand over their critical faculties to an outside authority, I’m not entirely convinced by either the conformity theory or the agentic state theory.
The theory of conformism comes from the work of Soloman Asch. It says that someone who has neither the ability nor the expertise to make decisions will let their in-group’s hierarchical authorities make the decisions. I call this the theory of the follower. It is everywhere around us, but it runs counter to what I see as America’s attempt to create a society of free individuals.
The agentic state theory is where Milgram went, and it says that under uncritical obedience an individual starts to view him/herself as the instrument for carrying out someone else’s wishes (an authority – a person, a group, an ideology, a god) and therefore no longer sees himself as responsible for his actions. It does make sense to me that once such a fundamental viewpoint change has happened, everything essentially bad about simple obedience to authority follows.
Both of these are descriptive. They don’t provide much on how to counteract some of the negative aspects of complicance with perceived authority. We desperately need some insights on how to break these tendencies. They tried to do it in the late sixties – there were some who really tried. It was a failure, ultimately.
I’ve sometimes wondered if the participants might have been frightened for themselves. In a context where someone was being hurt, the leverage of intimidation might have been under-analyzed. “Better him than me,” right? There is a subtle threatening aspect to certain forms of authority. Could a quick cost-benefit speculation figure into this at all? Did they feel that they could be punished in some way if they did not obey, if they were not compliant? Or are the majority of people really that easily manipulated?
This song can’t help but remind me of the mechanisms of social control at work in America today.
We often assume that there is some kind of ubiquitous “They” who determine what the “right thing to do” might be. “They” are rarely identified…
We’ve already allowed so much, but our fanaticism in various realms of ideology have been, and will continue to be, so very destructive. In college, I thought the theories that talked about “control of the masses” were quaint. That only seemed to apply to crazy places like the USSR. (I was young….)
Preachers of the past might have said that we are losing our souls, but some of the powerful reconstructionists and literalistic bible-thumpers and last-days people and others among the pseudoreligious right are among the most hurtful and powerful authoritarians that we have. They’re no help at all. And we worship Money – the circulation of capital leaving a a slash and burn zone whose results we are just beginning to harvest. And we have dehumanized other citizens of Earth as though they were some demonic Other to ourselves.

Education was my hope. Let’s just say that I’m not as optimistic about that anymore.
We have already nodded to torture and illegal surveillance and oppression and grandiose imperial ambitions and seizure of natural resources and so on and so on and so on. Our crimes are immense. We’re just trying to get through the day. Other people are in control, and it’s up to them. Many of us don’t even bother to find out about the issues. We haven’t thought about the results very much until it hit our pocketbooks. I wonder if anyone will ever describe us as the “good Americans.” What Milgram proved is that the Germans weren’t any worse than us.
We press the buzzer.
(Addendum after the first posting: Dar Williams did talk about “Buzzer” in the NPR interview. She described the experiment, and said that she has thought about it often over the years since she first found out about it in college. Later, she accidentally rear-ended a woman in a traffic accident and, because the woman was from New Haven, it reminded her about the Milgram experiment. Talking to her gave Dar Williams the outline of the character in the song. She felt that she was being responsible by doing what “she was supposed to do.” Then, having realized what that really meant, the woman was sensitized to that dynamic and wouldn’t participate in it again. It was transformative.)




